Prevention is better than cure, a rule of thumb that must be practiced in our daily life; other than that, it's an incredible way to keep your mind and body sound, but there are some ailments other than life-threatening diseases that need more attention, Hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating is one of them.
Hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating is not common in masses, but roughly 8 million Americans are still suffering. There are different ways to treat this condition, depending on the area where you sweat excessively and its severity.
These approaches are mainly adopted to treat this problem; these options may include antiperspirants, Botox injections, Laser treatment, or prescribed medications for excessive sweating. However, if the severity remains, concerned health professionals perform different medical devices or surgical procedures.
As per the experts, you need to be mindful that if a treatment is not working for your condition, it's just that your body needs another way of treatment or the dosage is not enough; sometimes, a combination of treatments works best and takes it under control.
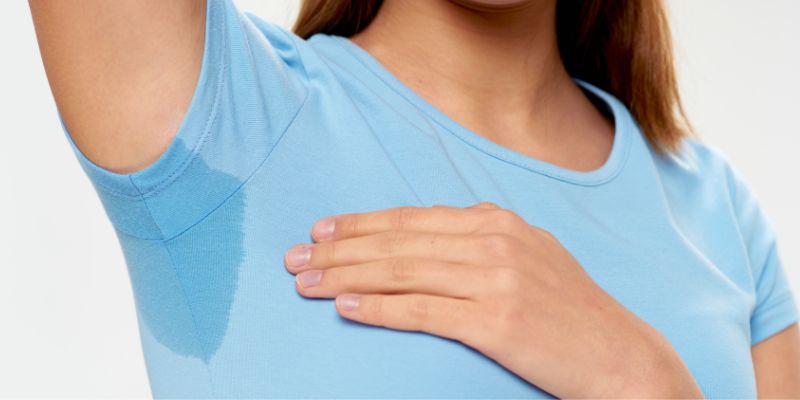

Hyperhidrosis Types and Symptoms
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition in which a person's body sweats excessively; hyper means"too much," and hidrosis is"sweating"; your body sweats more than it needs for cooling. The body area that sweats more may differ from one person to another; common areas are underarms, hands, feet, groin, buttocks, under the breast, and back.
Types of Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis falls into two categories: primary and secondary. Primary Hyperhidrosis starts at an early age or adolescence and does not happen due to other medical conditions. It is mostly inherited; people with a family history of excessive sweating are more prone to primary Hyperhidrosis.
Secondary Hyperhidrosis happens as a result or side effect of other medical illnesses. The most common conditions include Diabetes, Gout, Frosbite, head injury, tumor, overactive thyroid, obesity, and menopause. The secondary type may happen due to a side effect of supplements or medications; it may affect the whole body or some parts.
The common symptoms of Hyperhidrosis are visible sweating under normal conditions, excessive sweat on your hands or fingers that may interfere with your daily activities, and your skin turning soft, white, or peeling in certain areas, which may lead to skin infections in areas where you sweat heavily.

Treatment for Hyperhidrosis
The treatments for Hyperhidrosis are many, and the effectiveness of these treatments varies for different body types or areas. Your doctor prescribes suitable methods after examining the conditions. More than one treatment is also recommended in some cases as well. The common method for treating Hyperhidrosis is:
Antiperspirants
Antiperspirants are commonly used for controlling excessive sweat; they are temporary yet effective fixes and usually plug the sweat ducts, resulting in reduced sweating. Mostly, people use them as they are not costly or invasive. Antiperspirants are usually referred to as over-the-counter (OTC), but certain DRIs are a strong option and require a prescription, like Drysol, etc.
These are used for treating mild Hyperhidrosis; applying these to affected areas every night for three weeks or once in a while in a week or as prescribed by your doctor gradually decreases the excessive sweating. High-strength OT C and prescription antiperspirants may cause itching or burning if used incorrectly or without consulting the doctors. These are best for underarms, hands, and feet and are also effective for the face.
Topical Wipes
Topical wipes are considered best for the treatment of underarms; these wipes are effective for adults and children from age 9 or older after proper consultation. These wipes mostly contain anticholinergic medicine, which blocks the nerve signals that later are responsible for sweating. Usually, these medicines are available by prescription.
Botox
Botox is recommended when other treatments are not effectively producing the desired results; they are mostly performed on persons with severe primary Hyperhidrosis. Botox works perfectly by blocking the release of the chemicals that cause sweat glands to produce sweat.
Botox is injected right below the skin's surface, and it turns off sweating in that particular area; the FDA has approved its usage in other parts of the body, including hands, feet, face, and groin, but the treatment is recommended when all other options are not working. The procedure of injecting Botox must be performed by the health care professional with caution.
Laser
Laser is another option to treat Hyperhidrosis; many derma practitioners provide the option of laser treatment, which works best for underarms. The procedure includes using of laser to destroy the sweat glands via small incisions. The effectiveness of this treatment is not supported with definite evidence as these are performed on a relatively small group of people.
Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis is one of the oldest treatments for Hyperhidrosis, especially for feet and hands; usually, people undergoing iontophoresis get the treatment weekly. It is done with the help of an iontophoresis machine, which generates a low-voltage current that is applied to the affected area.
Usually, feet or hands are put in a pan of shallow water with low voltage current, and the current or device shuts down the sweat glands of your hands or feet. Special pads are placed on the treatment connected to the machine for parts other than hands or feet, and the function is performed. The health care professionals should perform this procedure; the side effects may include itching, irritation, or discomfort.
miraDry
miraDry got approval from the Food and Drug Administration authority in 2011; it's a handheld device used to prevent excessive sweating in your underarms and uses microwave energy to generate. This method is effective as users get instant results.
Oral Medications
Oral medications are prescribed medications approved by the FDA and are used to stop the excessive sweat in the underarms, hands, feet, groin, face, and other body parts. Most of these medicines are anticholinergics widely used to treat Hyperhidrosis and are very effective for mild sweating.
Surgery
Surgery might feel like a nightmare to people, but sometimes, it's your last resort when nothing else works. With the advancement in medical science, these procedures are not as painful as they seem; IHS-approved methods for underarms are as under:
- Excision: In this procedure, sweat glands are cut out
- Curettage: In this method scrapping technique is used to scrapes out the sweat glands
- Liposuction: Sweat glands are pulled out using suctions.
Sometimes, these surgical procedures are combined to get the desired results. ETS is another way to treat Hyperhidrosis, where a small camera is inserted under the armpit, damaging the nerve that connects with hyperactive sweat glands.
Conclusion
Hyperhidrosis is the sweating condition where your body produces excessive sweat, more than it needs to cool. It can both be inherited or result as a side effect from other ailment treatments; it can be triggered early, mostly in people with a family history of similar diseases.
But all these types of excessive sweating are curable through different methods, from medicines to surgery or the use of different medical devices, depending on the area and severity of the condition.